How Can I Prevent Cavities / Tooth Decay?
Cavities, also known as tooth decay, occur when plaque, the sticky substance that forms on teeth, combines with the sugars and / or starches of the foods that we eat. This combination produces acids that attack tooth enamel.
Follow these dental hygiene practices to prevent cavities:
-
Brush your teeth – In the fight against cavities, it is essential that you brush your teeth properly at least twice a day with a toothpaste containing fluoride.
-
Floss daily – Food debris gets caught in between our teeth when we eat. If the debris is not removed, it can lead to cavities. Flossing every day is the best way to remove food debris from in between the teeth.
-
Eat healthy – Proper nutrition plays an important role in good dental health. Eating nutritional snacks and limiting the amount of sugar intake will help to prevent plaque from forming on the teeth.
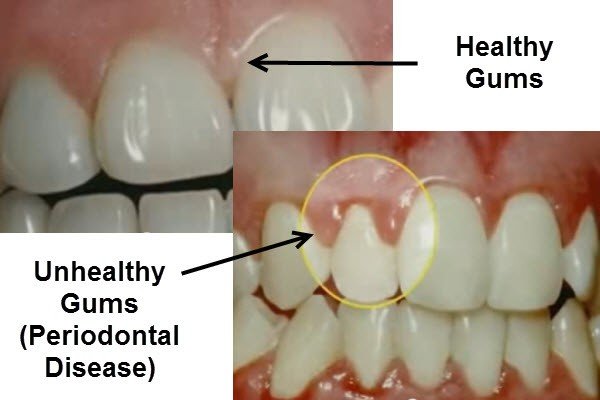
- Visit your dentist – Many cavities can only be detected by a dentist or a dental X-ray. Visiting your dentist for regular checkups and cleanings are a key factor in preventing cavities and staying on top of good oral hygiene.
-
Have sealants placed – Dental sealants are a protective coating that is applied to the biting surfaces of the back teeth. The sealant protects the tooth from getting a cavity by shielding against bacteria and plaque. Sealants are more common in children because of the new growth of permanent teeth; however, sealants can benefit adults too.
-
Use a mouthwash – There are several antimicrobial mouthwashes on the market that have been clinically proven to reduce plaque. Rinsing with one of these mouthwashes after brushing or eating can aid in cavity prevention.
-
Chew sugarless gum – Believe it or not, chewing certain sugarless gums can actually help to prevent cavities by increasing the flow of saliva in your mouth.
It is especially important to keep an eye on how often your child eats as well as what he/she eats. You should limit between-meal snacks to reduce the number of acid attacks on teeth and to give teeth a chance to repair themselves. Limit their intake of candies, cookies, soda and other sugary drinks. Make sure your child doesn’t eat or drink anything with sugar after bedtime tooth brushing. Don’t forget to supervise young children when they brush. Since most cavities in children and adolescents develop in the molars, it’s best to get these teeth sealed as soon as they come in.
Ref: www.dentistry.com
www.nidcr.nih.gov