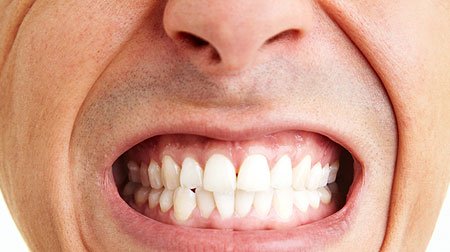
How To Stop Teeth Grinding? Causes and Treatments
Teeth grinding or bruxism is the involuntary clenching, grinding and gnashing of the teeth. Some people are regular, forceful tooth grinders. Often it happens during sleep, but some people grind their teeth when they are awake. Teeth grinding can be a result of stress. For example, some people grind their teeth when they are angry, concentrating or feeling anxious. It can occur in both children and adults.
Effects of teeth grinding
-
Cracked tooth enamel
-
More wear and tear on the teeth than is normal
-
Broken teeth or broken restorations (for example, fillings)
-
Strain on the jaw joint
-
Pain in the jaw joint or limited movement
-
Tooth loss (rare)
Causes of teeth grinding
-
Emotional stress, such as anger or anxiety
-
Mental concentration
-
Physical stress, such as illness, poor nutrition or long-term pain
-
Some dental treatments, such as fillings that sit ‘too high’
-
When teeth are coming through in babies and children
-
Taking antipsychotic or antidepressant medications
-
Regularly drinking alcohol, smoking and using recreational drugs such as ecstasy and cocaine
Treatment for teeth grinding
If you think you grind your teeth, see your dentist or other oral health professionals as soon as possible. They will look at your teeth and talk about possible treatment options that may include:
-
Repair of tooth damage
-
Fixing fillings that are too high
-
A special mouth guard (‘bite splints’) to wear at night so that the guard is worn down instead of your teeth.
Other treatments may include stress management therapy, relaxation techniques, cognitive behavior therapy etc.
In case of teeth grinding, you may seek help from your dental clinic, your doctor, psychologist or from a physiotherapist depending on the cause of teeth grinding.
Ref: www.nhs.uk/conditions/teeth-grinding
www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au